Matrix
Techniques in Optics
Transfer
Matrix for Refraction at a Plane (Curved) Surface
In the case of the plane surface, the position of the ray at the refracting surface does not change but the angle does, according to Snell's Law. If the ray goes from a medium of index of refraction 1 to that of index of refraction n, we have:
Again, make use of the small angle approximation to arrive at:
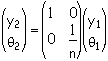
The the surface has radius of curvature R, the corresponding relationship is:
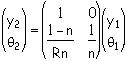
Obviously, the relation for the plane surface can be recovered by letting R go to infinity.