Matrix
Techniques in Optics
Transformation
Matrix for a Thin Converging Lens
Look at the figure below for a converging lens with focal length f. We are making the thin lens approximation - i.e. the thickness of the lens is zero. Notice that in this case the angle of the ray changes before and after the element but the vertical entry and exit position ( y1 = y2 = y) do not. This is in contrast to the above example of the drift space.
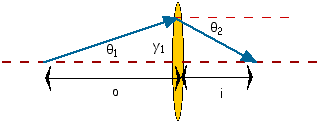
We start with:
![]()
![]()
![]()
In the last step we made use of the small angle approximation. Note the sign of the angle: if the incident angle is positive, then the emergent angle is negative. From this we can write the matrix relationship:
For a diverging lens, replace f by -f.